Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all
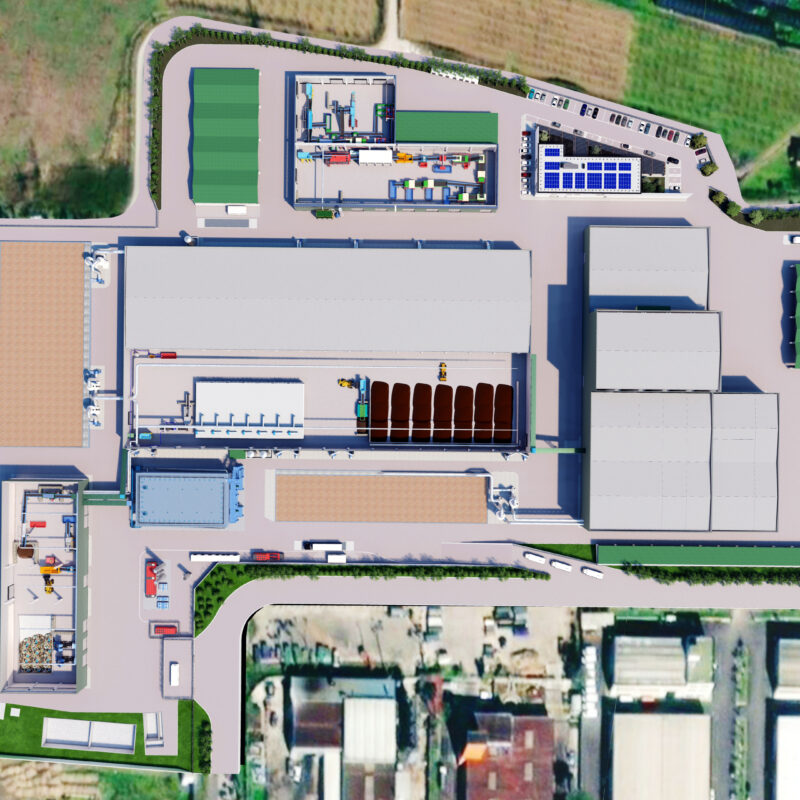
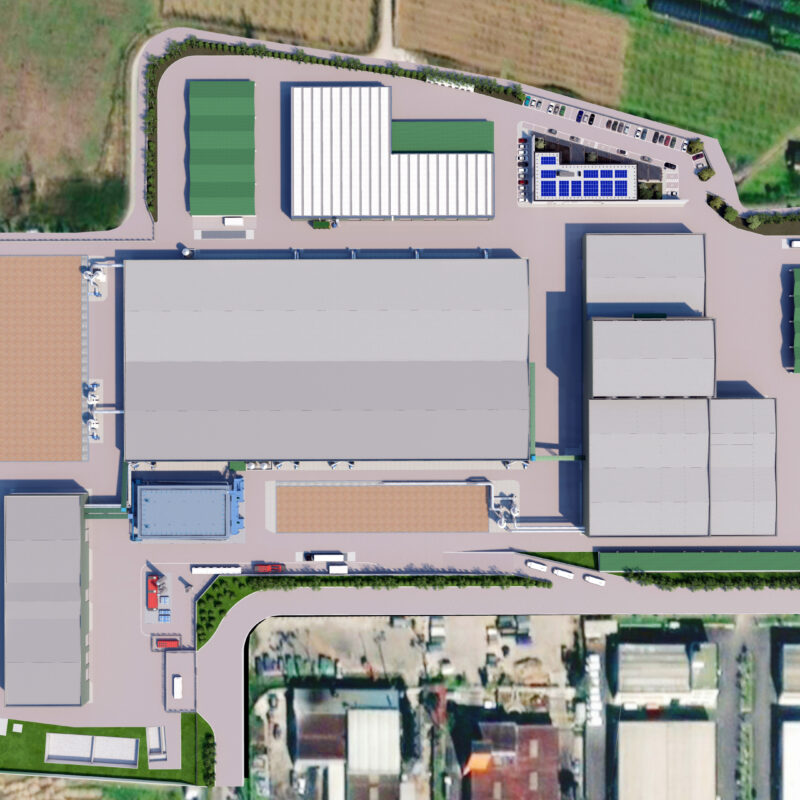
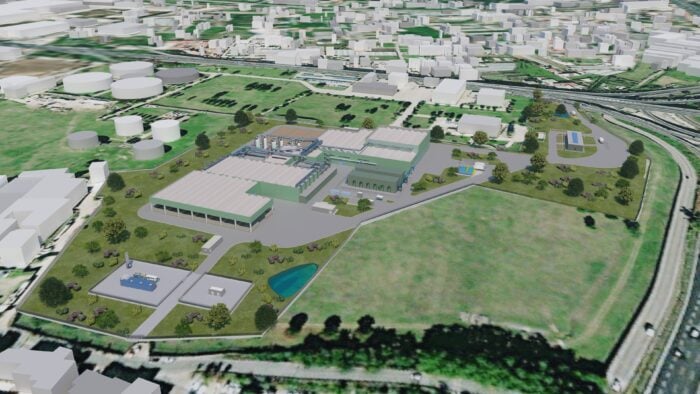
Making the most of the EU Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF) instrument, the project provides an upgrade to the plant layout in order for it to meet the increasingly stringent environmental regulations and maximize recovery and recycling rates. The initiative broadly contributes to enhancing the integrated cycle of urban waste.
Location
Giugliano (NA)
Data
Type of service:
Technical and economic feasibility design
Design period:
December 2021
Technical data
Total site surface:
60.000 m²
Aerobic-anaerobic OFMSW section
Treatment capacity: 75.700 t/year
Produced Compost: 10.500 t/year
Produced Biomethane: 600 Sm3/h
Paper and cardboard recovery line
Treatment capacity: 37.200 t/year
Plastic material bales: 2.400 t/year
Paper and Cardboard bales: 29.000 t/year
Glas recovery line
Treatment capacity:77.000 t/year
Green glass cullet: 26.250 t/year
Flint glass cullet: 26.250 t/year
Amber glass cullet: 13.130 t/year
Metals (ferrous and non-ferrous): 875 t/year
The plant produces biomethane for the transport sector and compost for agricultural use in compliance with European and national regulations (EU regulation EN:13432 and the new European fertilizer regulation 2019/1009).
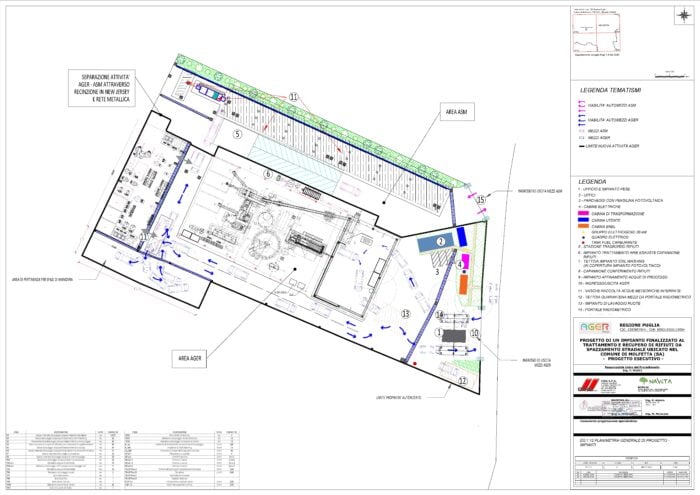
The revamp will include three process lines:
- An aerobic-anaerobic treatment section for the Organic Fraction of the Municipal Solid Waste (OFMSW) that will recover high-quality compost and biomethane;
- A section for the recovery of paper and cardboard coming from municipal solid waste segregated at source;
- A section for the recovery of glass coming from municipal waste segregated at source (colour-sorted glass, cullet production).
The aerobic-anaerobic process line provides a waste treatment capacity equal to 57.000 t/y of OFMSW, and 18.700 t/y of green waste. The section consists of:
a) A reception bunker followed by mechanical pre-treatment of incoming waste;
b)An anaerobic digestion section, where biomass undergoes a biochemical conversion producing biogas and a residual liquid (digestate);
c) A digestate mechanical dewatering section, with subsequent flocculation and flotation treatment followed by a leachate treatment plant;
d)A composting section for the aerobic stabilization of the solid digestate, thus obtaining a quality compost;
e) An up-grading unit of the biogas produced by anaerobic digestion to bio-methane production.